Abstract
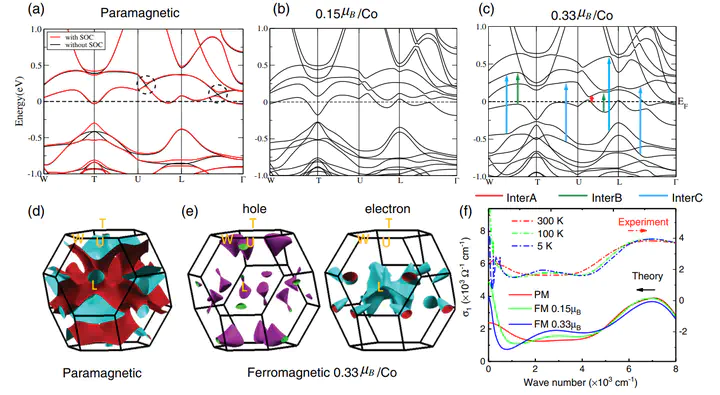
The discovery of magnetic Weyl semimetal (magnetic WSM) in Co3Sn2S2 has triggered great interest for abundant fascinating phenomena induced by band topology conspiring with the magnetism. Understanding how the magnetization affects the band structure can give us a deeper comprehension of the magnetic WSMs and guide us for the innovation in applications. Here, we systematically study the temperature-dependent optical spectra of ferromagnetic WSM Co3Sn2S2 experimentally and simulated by first-principles calculations. Our results indicate that the many-body correlation effect due to Co 3d electrons leads to the renormalization of electronic kinetic energy by a factor about 0.43, which is moderate, and the description within density functional theory is suitable. As the temperature drops down, the magnetic phase transition happens, and the magnetization drives the band shift through exchange splitting. The optical spectra can well detect these changes, including the transitions sensitive and insensitive to the magnetization, and those from the bands around the Weyl nodes. The results support that, in magnetic WSM Co3Sn2S2 , the bands that contain Weyl nodes can be tuned by magnetization with temperature change.